Symptoms of Athlete’s Foot
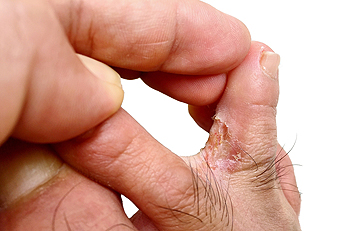 If you notice a rash on your foot, you may have a condition that is known as athlete’s foot. It is a common fungal infection that is contagious, however there are methods that can be implemented which may prevent athlete’s foot from developing. This type of fungus lives and thrives in moist and warm environments, which can include public swimming pools, communal showers, locker rooms, and surrounding areas. It is beneficial to wear appropriate shoes while in these types of places, as it may prevent the fungus from touching the skin. Common symptoms that are typically associated with this ailment can include dry skin between the toes and on the bottom of the feet, as well as severe itching. Additionally, in more severe cases, the skin may peel and crack, and the skin between the toes may burn. If you are afflicted with athlete's foot, it is strongly advised that you seek the counsel of a podiatrist who can guide you toward the proper treatment.
If you notice a rash on your foot, you may have a condition that is known as athlete’s foot. It is a common fungal infection that is contagious, however there are methods that can be implemented which may prevent athlete’s foot from developing. This type of fungus lives and thrives in moist and warm environments, which can include public swimming pools, communal showers, locker rooms, and surrounding areas. It is beneficial to wear appropriate shoes while in these types of places, as it may prevent the fungus from touching the skin. Common symptoms that are typically associated with this ailment can include dry skin between the toes and on the bottom of the feet, as well as severe itching. Additionally, in more severe cases, the skin may peel and crack, and the skin between the toes may burn. If you are afflicted with athlete's foot, it is strongly advised that you seek the counsel of a podiatrist who can guide you toward the proper treatment.
Athlete’s Foot
Athlete’s foot is often an uncomfortable condition to experience. Thankfully, podiatrists specialize in treating athlete’s foot and offer the best treatment options. If you have any questions about athlete’s foot, consult with one of our podiatrists from Coastal Foot & Ankle Wellness Center, LLC. Our doctors will assess your condition and provide you with quality treatment.
What Is Athlete’s Foot?
Tinea pedis, more commonly known as athlete’s foot, is a non-serious and common fungal infection of the foot. Athlete’s foot is contagious and can be contracted by touching someone who has it or infected surfaces. The most common places contaminated by it are public showers, locker rooms, and swimming pools. Once contracted, it grows on feet that are left inside moist, dark, and warm shoes and socks.
Prevention
The most effective ways to prevent athlete’s foot include:
- Thoroughly washing and drying feet
- Avoid going barefoot in locker rooms and public showers
- Using shower shoes in public showers
- Wearing socks that allow the feet to breathe
- Changing socks and shoes frequently if you sweat a lot
Symptoms
Athlete’s foot initially occurs as a rash between the toes. However, if left undiagnosed, it can spread to the sides and bottom of the feet, toenails, and if touched by hand, the hands themselves. Symptoms include:
- Redness
- Burning
- Itching
- Scaly and peeling skin
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis is quick and easy. Skin samples will be taken and either viewed under a microscope or sent to a lab for testing. Sometimes, a podiatrist can diagnose it based on simply looking at it. Once confirmed, treatment options include oral and topical antifungal medications.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact one of our offices located in St. Augustine, and Palatka, FL . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
Athlete's Foot
Athlete’s foot is an extremely contagious infection caused by a fungus that results in itching, burning, dry, and flaking feet. The fungus that causes athlete’s foot is known as tinea pedis and thrives in moist, dark areas such as shower floors, gyms, socks and shoes, commons areas, public changing areas, bathrooms, dormitory style houses, locker rooms, and public swimming pools. Athlete’s foot is difficult to treat as well because of the highly contagious and recurrent nature of the fungus.
Tinea is the same fungus that causes ringworm, and is spread by direct contact with an infected body part, contaminated clothing, or by touching other objects and body parts that have been exposed to the fungus. Because the feet are an ideal place for tinea to grow and spread, this is the most commonly affected area. It is, however, known to grow in other places. The term athlete’s foot describes tinea that grows strictly on the feet.
The most commonly infected body parts are the hands, groin, and scalp, as well as the feet. Around 70% of the population suffer from tinea infections at some point in their lives, however not all of these cases are athlete’s foot. Just like any other ailment, some people are more likely to get it than others, such as people with a history of tinea infections or other skin infections, both recurring and non-recurring ones. The extent to which a person experiences regrowth and recurrent tinea infections varies from person to person.
Sometimes people will not even know that they are infected with tinea or that they have athlete’s foot because of a lack of symptoms. However, most experience mild to moderate flaking, itching, redness, and burning. However, some of the more severe symptoms include cracking and bleeding skin, intense itching and burning, pain while walking or standing, and even blistering.
Because of the recurring nature of the tinea fungus and the athlete’s foot it causes, the best way to treat this condition is with prevention. You can take some preventative measures such as wearing flip flops or sandals in locker rooms and public showers to reduce contact with the floor. It also helps to keep clean, dry feet while allowing them to breathe. Using powders to keep your feet dry is a good idea, as well as keeping your feet exposed to light and cool air, to prevent the growth of tinea. If you do happen to get athlete’s foot, opt for using topical medicated creams, ointments or sprays. These treatments help eliminate and prevent it from coming back.
Ingrown Toenails
Ingrown toenails (onychocryptosis) are a common foot ailment and it is very unpleasant to experience. The condition is caused by an increase in pressure from the ingrowth of the nail edge into the skin of the toe. Ingrown toenails commonly cause pain in those who experience them. In some cases, the skin surrounding the ingrown toenail may break which may lead bacteria to enter through and cause an infection. Common symptoms of this ailment include pain, redness, swelling, and warmth around the toe.
An imbalance between the size of the nail and the enlargement of the nail skin edge causes ingrown toenails. This condition is often caused by improperly trimming the toenails. If you are trying you cut your nails, you should always try to trim straight across instead of in a rounded shape. Ingrown toenails can also be an inherited condition and they may also be caused by improper shoe fitting.
Another common cause of the condition is wearing shoes that are either too small or too large. Other causes include poor foot hygiene, obesity, diabetes, arthritis, edema, and fungal infections. There are many risk factors that may make a person more likely to develop an ingrown toenail. Athletes who play “stop and start” sports such as tennis, soccer, and basketball are most likely to have ingrown toenails.
People who have diabetes, a compromised immune system, or poor circulation should immediately seek care from a podiatrist if they have an ingrown toenail. It is also recommended to seek professional assistance if at-home remedies are not successful within a week or if there is persistent pain.
Painful Joint Pain in the Feet
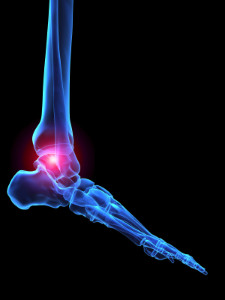 The medical condition that is referred to as rheumatoid arthritis can affect the tissues in the joints of the feet as a result of a compromised immune system. The symptoms that generally accompany this ailment can consist of stiffness, severe pain, and difficulty walking. Many patients notice a constant achy feeling in their feet as the day progresses, and the feet may feel warm. There are specific parts of the foot that are typically impacted by this condition. These can include the small joints that are located between the bones in the toes, the ankle joint, and the joints that surround the heel bone. Treatment options to be considered can include soaking the affected foot in warm water which may help in reducing existing inflammation, or wearing a boot that may help to relieve pressure. If you are afflicted with this painful condition, it is strongly advised that you consult with a podiatrist who can choose the correct treatment for you.
The medical condition that is referred to as rheumatoid arthritis can affect the tissues in the joints of the feet as a result of a compromised immune system. The symptoms that generally accompany this ailment can consist of stiffness, severe pain, and difficulty walking. Many patients notice a constant achy feeling in their feet as the day progresses, and the feet may feel warm. There are specific parts of the foot that are typically impacted by this condition. These can include the small joints that are located between the bones in the toes, the ankle joint, and the joints that surround the heel bone. Treatment options to be considered can include soaking the affected foot in warm water which may help in reducing existing inflammation, or wearing a boot that may help to relieve pressure. If you are afflicted with this painful condition, it is strongly advised that you consult with a podiatrist who can choose the correct treatment for you.
Because RA affects more than just your joints, including the joints in your feet and ankles, it is important to seek early diagnosis from your podiatrist if you feel like the pain in your feet might be caused by RA. For more information, contact one of our podiatrists of Coastal Foot & Ankle Wellness Center, LLC. Our doctors will assist you with all of your podiatric concerns.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s own immune system attacks the membranes surrounding the joints. Inflammation of the lining and eventually the destruction of the joint’s cartilage and bone occur, causing severe pain and immobility.
Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Feet
Although RA usually attacks multiple bones and joints throughout the entire body, almost 90 percent of cases result in pain in the foot or ankle area.
Symptoms
- Swelling and pain in the feet
- Stiffness in the feet
- Pain on the ball or sole of feet
- Joint shift and deformation
Diagnosis
Quick diagnosis of RA in the feet is important so that the podiatrist can treat the area effectively. Your doctor will ask you about your medical history, occupation, and lifestyle to determine the origin of the condition. Rheumatoid Factor tests help to determine if someone is affected by the disease.
If you have any questions please feel free to contact one of our offices located in St. Augustine, and Palatka, FL . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.
Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Feet
Although rheumatoid arthritis attacks multiple bones and joints throughout the entire body, ninety percent of people who actually develop this condition usually do so in the foot or ankle area. Those who develop this kind of arthritis in the feet usually develop symptoms around the toes and forefeet first, before anywhere else. Rheumatoid arthritis appears to have a genetic component. If it runs in the family, then you will be more likely to develop it as well.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s own immune system attacks the lining of the membranes surrounding the joints. This causes inflammation of the membrane lining, and the gradual destruction of the joint’s cartilage and even bone.
Some of the most common symptoms that are associated with RA include pain and swelling of the feet. Stiffness in the feet is also another common symptom that people experience. Those who have RA in the feet usually feel the pain in the ball or sole of their feet. This can get to be very painful at times. A person's joints can even shift and become deformed after a period of time.
In order to properly diagnose RA in the feet it is usually necessary for a doctor or podiatrist to evaluate the area. Your doctor will also question you about your medical history, occupation, etc., to determine whether anything in your lifestyle may have triggered the condition. There are a number of tests that may be performed to help diagnose RA, such as a rheumatoid factor test. There is, however, no one single test that will tell you for sure if you have RA. There are different X-rays that can be taken as well to determine if a person has RA in their feet.
There is a range of treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis. Treatment of RA is usually a lifelong process that includes a variety of methods of treatment and therapy. Your doctor can prescribe special shoes that should help with arch support as well as heel support. A physical therapist can help those with this condition learn exercises which will keep their joints flexible. Surgery may be needed to correct some of the issues with the feet, such as bunions, and hammertoes. Fusion is usually the most successful surgical option for rheumatoid arthritis. However, people need to keep in mind that there are some risks associated with these surgeries.
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain. The plantar fascia is the thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes. When this band of connective tissue becomes inflamed, plantar fasciitis occurs. Fortunately, this condition is treatable.
There are several factors that may put you at a greater risk for developing plantar fasciitis. One of the biggest factors is age; plantar fasciitis is common in those between the ages of 40 to 60. People who have jobs that require them to be on their feet are also likely to develop plantar fasciitis. This includes factory workers, teachers, and others who spend a large portion of their day walking around on hard surfaces. Another risk factor is obesity because excess weight can result in extra stress being placed on the plantar fascia.
People with plantar fasciitis often experience a stabbing pain in the heel area. This pain is usually at its worst in the morning, but can also be triggered by periods of standing or sitting. Plantar fasciitis may make it hard to run and walk. It may also make the foot feel stiff and sensitive, which consequently makes walking barefoot difficult.
Treatment for plantar fasciitis depends on the severity of the specific case of the condition. Ice massage applications may be used to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy is often used to treat plantar fasciitis, and this may include stretching exercises. Another treatment option is anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen.
If you suspect that you have plantar fasciitis, meet with your podiatrist immediately. If left untreated, symptoms may lead to tearing and overstretching of the plantar fascia. The solution is early detection and treatment. Be sure to speak with your podiatrist if you are experiencing heel pain.
Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Poor Blood Circulation in the Feet
Poor blood circulation in the feet and legs is often caused by peripheral artery disease (PAD), which is usually the result of a buildup of plaque in the arteries. Plaque buildup, or atherosclerosis, can be the result of excess calcium and cholesterol in the bloodstream. This restricts how much blood can flow through arteries. Reduced blood flow to a certain area of the body severely limits the amount of oxygen and nutrients that part of the body receives. This leads to degeneration in the muscles and other tissues. Sometimes, poor blood circulation in the feet and legs can be caused by other conditions, such as the damaging or inflammation of blood vessels, known as vasculitis.
The lack of oxygen and nutrients caused by poor blood circulation can restrict muscle growth and development, as well as cause muscle pain and cramps, weakness, and stiffness. Other common symptoms include numbness in the legs and feet, skin discoloration in the affected limbs, slower nail and hair growth, and erectile dysfunction in men. In more severe cases of PAD, pain can be present even when a person isn't exercising, and may range from mildly uncomfortable to completely debilitating.
Poor blood circulation in the feet and legs is more common in those who are overweight or obese, have diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, who smoke, or who have a family history of PAD or related conditions such as a heart attack, stroke, etc. Diabetes and smoking place a person at greatest risk for developing poor blood circulation, although advanced age, over 50, can also increase risk.
If you are experiencing poor blood circulation in the feet and legs caused by PAD, it is important to make changes to your lifestyle in order to reduce your risk of experiencing a heart attack or stroke caused by this condition. If you smoke, quit completely. This will increase the amount of oxygen in your bloodstream. Exercising and reducing the saturated fats in your diet. Saturated fats come from fatty meats, fried foods, whole milk, etc., can make a difference in improving blood circulation in feet. It is also important to avoid developing influenza and to carefully control your blood sugar if you have diabetes.
Your doctor may recommend combining lifestyle changes with a prescription medication regimen to improve blood circulation. The most commonly-used medications for PAD are called statins and work by blocking the amount of enzymes in your body that produce cholesterol. They are known by the brand names Zocor, Lipitor, Crestor, and others.
Bunions
A bunion is an enlargement of the base joint of the toe that connects to the foot, often formed from a bony growth or a patch of swollen tissues. It is caused by the inward shifting of the bones in the big toe, toward the other toes of the foot. This shift can cause a serious amount of pain and discomfort. The area around the big toe can become inflamed, red, and painful.
Bunions are most commonly formed in people who are already genetically predisposed to them or other kinds of bone displacements. Existing bunions can be worsened by wearing improperly fitting shoes. Trying to cram your feet into high heels or running or walking in a way that causes too much stress on the feet can exacerbate bunion development. High heels not only push the big toe inward, but shift one's body weight and center of gravity towards the edge of the feet and toes, expediting bone displacement.
A podiatrist knowledgeable in foot structure and biomechanics will be able to quickly diagnose bunions. Bunions must be distinguished from gout or arthritic conditions, so blood tests may be necessary. The podiatrist may order a radiological exam to provide an image of the bone structure. If the x-ray demonstrates an enlargement of the joint near the base of the toe and a shifting toward the smaller toes, this is indicative of a bunion.
Wearing wider shoes can reduce pressure on the bunion and minimize pain, and high heeled shoes should be eliminated for a period of time. This may be enough to eliminate the pain associated with bunions; however, if pain persists, anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed. Severe pain may require an injection of steroids near the bunion. Orthotics for shoes may be prescribed which, by altering the pressure on the foot, can be helpful in reducing pain. These do not correct the problem; but by eliminating the pain, they can provide relief.
For cases that do not respond to these methods of treatment, surgery can be done to reposition the toe. A surgeon may do this by taking out a section of bone or by rearranging the ligaments and tendons in the toe to help keep it properly aligned. It may be necessary even after surgery to wear more comfortable shoes that avoid placing pressure on the toe, as the big toe may move back to its former orientation toward the smaller toes.